Assessing patient inspiratory flow rate for clinical efficacy with Bufomix (Budesonide/Formoterol) Easyhaler®
Insights | 28/02/2022Prescribing information available here and Adverse Event Reporting information can be found at the bottom of the page
- Choosing an inhaler for patients with limited inspiratory effort, such as children, the elderly, and COPD patients, requires careful consideration.
- Bufomix Easyhaler® provides accurate and consistent dose delivery even with low patient inhalation flow rates, starting from a peak inspiratory flow (PIF) of 30 L/min.1
- A patient training device, for instance In-Check DIAL G16, may help to evaluate patients’ inspiratory effort and to ensure clinical efficacy with the selected inhaler.
Inhalation is the recommended route of administration when treating chronic respiratory diseases such as asthma and COPD. All dry powder inhalers (DPIs) use the patient’s own inspiratory effort for pulmonary drug delivery. However, the optimal inhalation flow rate required for effective lung deposition also depends on the properties of the inhaler and varies considerably between different devices. Some patients, like young children, the elderly, and patients with COPD, may have difficulties in reaching the high inspiratory flow rates required by certain DPI devices. It is essential to assess the patient’s pulmonary function and select the most appropriate inhaler individually for each patient in order to ensure efficient therapy.1–3
Evidence from in-vitro and in-vivo studies suggests that Bufomix Easyhaler provides accurate and consistent dosing even for patients with low inhalation flow rates4 in asthma and COPD patients of varying age and disease severity5,6 An inspiratory flow rate of 30L/min has been reported as optimal for Easyhaler usage1 . These studies support the selection of Easyhaler therapy for children (6 years and older), the elderly and patients with COPD
In some cases, for example with patients having severe airway obstruction, further evaluation of a patient’s inspiratory effort might support the selection of an inhaler. Patient training devices, such as In-Check DIAL G16, help to assess the patient’s inspiratory flow rate. In-Check DIAL is an inspiratory peak flow meter that can be set to imitate the internal resistance of, and the appropriate inhalation required by, different pressurised metered dose inhalers (pMDIs) and DPIs, including Easyhaler.7
To reliably estimate the patient’s ability to produce sufficient inspiratory airflow, it is of importance to adjust the In-Check DIAL device on the correct setting. Bufomix Easyhaler® combination therapy is a medium-to-high resistance device8. When assessing patient inspiratory flow rate with Bufomix Easyhaler®, the medium to high resistance setting should be used. Inspiratory flow rates starting from 30L/min are adequate to get a full dose of Bufomix Easyhaler® medication and generally associated with clinical efficacy.1,3,5,6
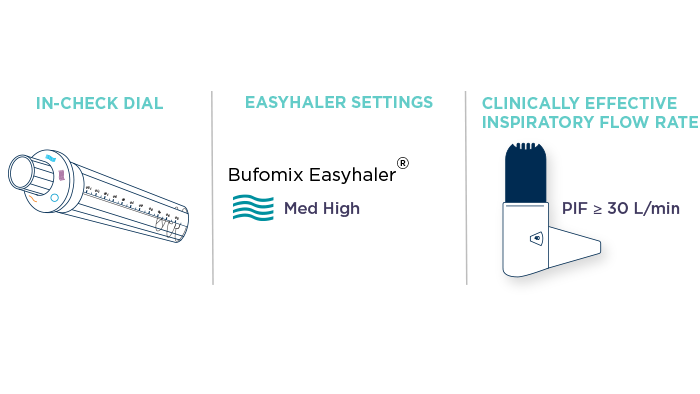
Figure 1. Assessment of patient inspiratory flow rate for clinical efficacy with Easyhaler® using In-Check DIAL G16. With Easyhaler, optimal drug delivery is achieved even with low patient inhalation flow rates, starting from an inspiratory flow rate of 30 L/min.
References:
- Ghosh S, Ohar JA, Drummond MB. Peak inspiratory flow rate in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: Implications for dry powder inhalers. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv 2017;30(6):381–387.
- Haidl P, Heindl S, Siemon K, Bernacka M, Cloes RM. Inhalation device requirements for patients' inhalation maneuvers. Respiratory Medicine 2016;118,65–75.
- Laube BL, Janssens HM, de Jongh FHC, Devadason SG, Dhand R, Diot P, Everard ML, Hovarth I, Navalesi P, Voshaar T, Crystyn H. What the pulmonary specialist should know about the new inhalation therapies. Eur Respir J 2011;37:1308–1331.
- Haikarainen J, Selroos O, Löytänä T, Metsärinne S, Happonen A, Rytilä P. Budesonide/formoterol EasyhalerÒ: Performance under simulated real-life conditions. Pulm Ther 2017;3:125–138.
- Malmberg LP, Everard ML, Haikarainen J, Lähelmä S. Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo flow rate dependency of budesonide/formoterol Easyhaler®. J Aerosol Med Pulm Drug Deliv 2014;27(5):329–40.
- Malmberg LP, Rytilä P, Happonen P, Haahtela T. Inspiratory flows through dry powder inhaler in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: age and gender rather than severity matters. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis 2010;9(5):257–62.
- Sanders MJ. Guiding inspiratory flow: Development of the In-Check DIAL G16, a tool for improving inhaler technique. Pulm Med 2017:1495867.
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2213219820310047?ref=pdf_download&fr=RR-2&rr=858732201f2479e5
Date of preparation: December 2025 / EASYH-2113(2)
Bufomix Easyhaler Contraindications and Undesirable effects
Contraindications:
Hypersensitivity to the active substances or lactose monohydrate (which contains small amounts of milk protein).
Undesirable Effects:
Common (≥1/100 to < 1/10): Candida infections in the oropharynx, pneumonia (in COPD patients) headache, tremor, palpitations, mild irritation in the throat, coughing, dysphonia including hoarseness.
See SmPC for full list of adverse reactions
| Adverse effects should be reported. You can report side effects directly via the Health Products Regulatory Authority (HPRA) website: www.hpra.ie or by email on medsafety@hpra.ie. Adverse effects should also be reported to Orion Pharma via ie.medicalinformation@orionpharma.com |

